Camera
1) Pin-hole camera
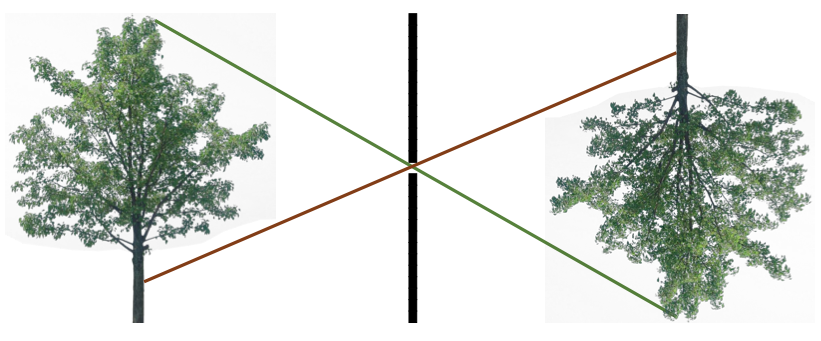
- Pin-hole camera model is a widely used camera model in computer vision.
- It collects light through a small hole to the inside of dark box or room.
- Light passes through a single point, the camera center, C, before it is projected onto an image plane.
2) Lens camera
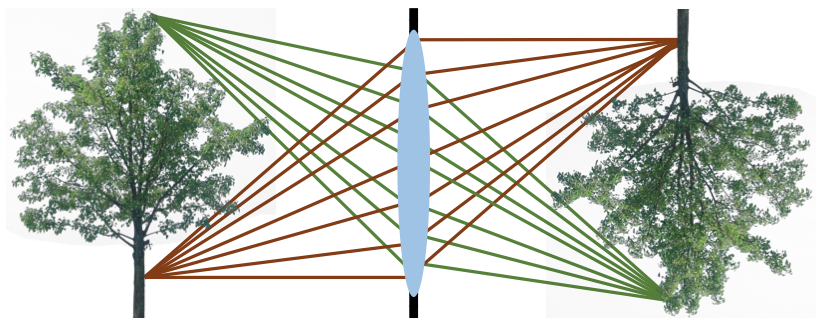
- Lenses map bundles of rays from points on the scene to the sensor.
3) Common feature
- only use central rays.
- assume the lens camera is in focus.
4) difference
- pin-hole camera : focal length is distance between aperture (hole) and sensor.
- lens camera : focal length is distance where parallel rays intersect.
Camera matrix
1) 개요
- A camera is a mapping from the 3D world to a 2D image.
2) 수식적 이해
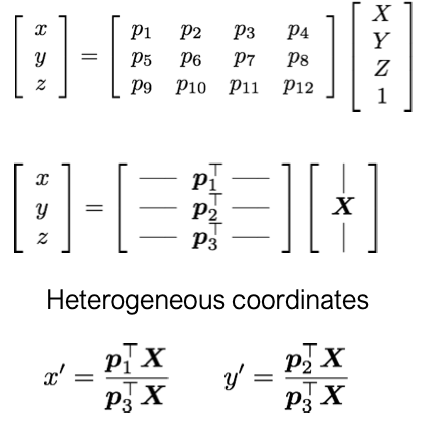
$$x = PX$$
$$\begin{bmatrix}x\\y\\z \end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix} p_{1}& p_{2} & p_{3} & p_{4} \\p_{5}& p_{6} & p_{7} & p_{8}\\p_{9}& p_{10} & p_{11} & p_{12} \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}X\\Y\\Z\\1 \end{bmatrix} $$
- X : homogeneous world coordinates
- P : camera matrix
- x : homogeneous image coordinates

$$P = \begin{bmatrix} f & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & f & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} I & | & 0\end{bmatrix}$$
3) Generalizing the camera matrix
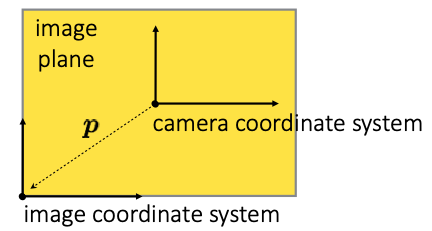
- In particular, the camera and image origin may be different.
$$P = K[I|0], \; K = \begin{bmatrix} f & 0 & c_{x} \\ 0 & f & c_{y} \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$
- c_x, c_y : image point where the optical axis intersects the image plane.
4) world to camera coordinate system transformation
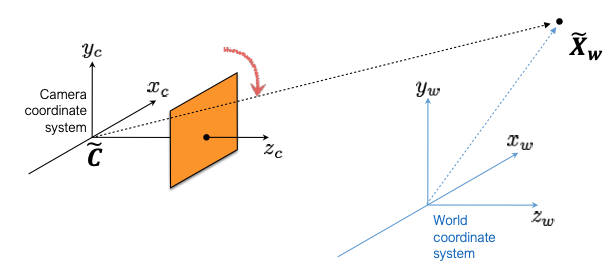
$$\tilde{X}_{w} - \tilde{C}$$
- translate the world coordinate to camera coordinate
$$R \cdot \tilde{X}_{w} - \tilde{C}$$
- rotate the translated point to be aligned.
$$\tilde{X}_{c} = R \cdot (\tilde{X}_{w} - \tilde{C})$$
- The above equation is the heterogeneous coordinates.
- In homogeneous coordinates,
$$\begin{bmatrix} X_{c} \\ Y_{c} \\ Z_{c} \\ 1 \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} R & -RC \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} X_{w} \\ Y_{w}\\ Z_{w} \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \;\; or \;\; X_{c} = \begin{bmatrix} R & -R\tilde{C} \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} X_{w}$$
5) General pinhole camera matrix
- combine camera matrix in camera coordinate system with camera matrix aligned with world coordinates.
$$x = PX_{c} = K[I|0]X_{c}, \;\;\; X_{c} = \begin{bmatrix} R & -R\tilde{C} \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} X_{w}$$
$$x = PX_{w}$$
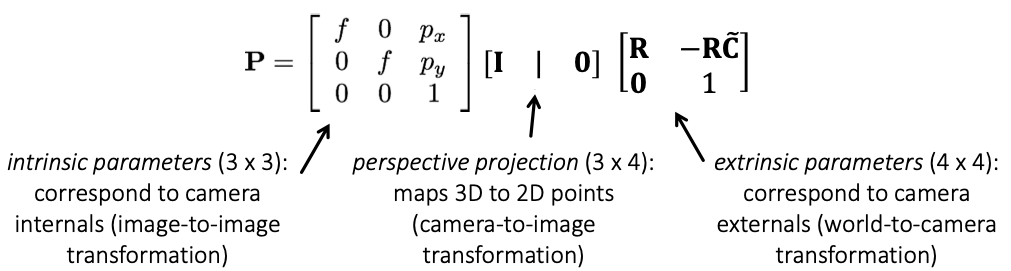
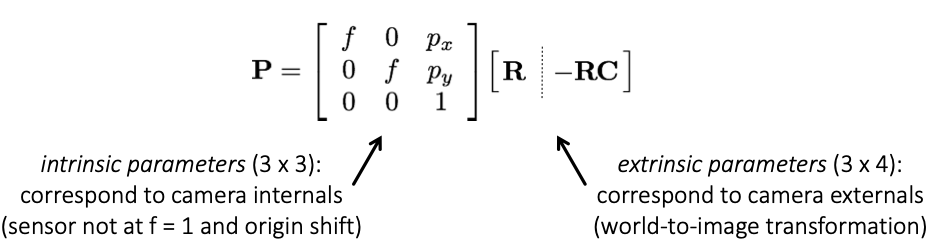
$$P = K[R|t], \;\; t = -RC$$
- R : rotation matrix describing the orientation of the camera.
- t : 3D translation vector describing the position of the camera center.
- K : intrinsic calibration matrix which describes the projection properties of the camera.
- if the camera and world have the same coordinate system, [R|t] will be an identity.
Perspective distortion
1) 개요
- pinhole camera and all of the more general cameras have perspective distortion.
- Perspective distortion magnification changes with depth.

Orthographic projection
1) 개요

$$P = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$
- distance from the center of projection to the projection plane is infinite
- constant magnification is equal to 1.
- no shift between camera and image origins.
- world and camera coordinate systems are the same.
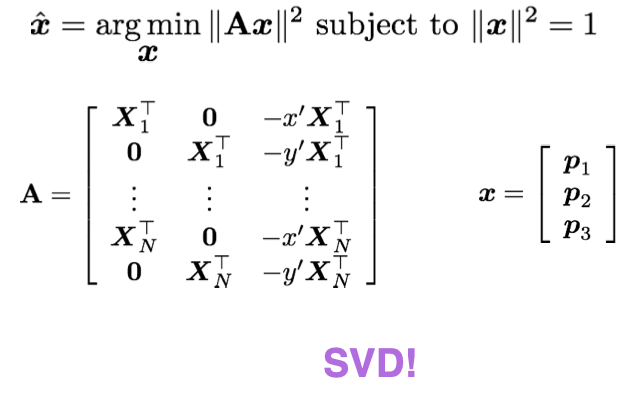
Geometric camera calibration
- find a camera matrix
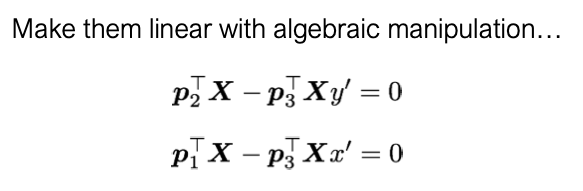
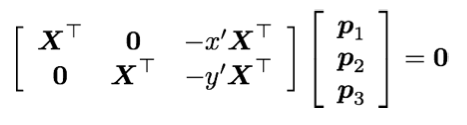

ref.
www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs5670/2019sp/lectures/lec10_cameras.pdf
'AI > Computer Vision' 카테고리의 다른 글
| RANSAC (0) | 2021.04.06 |
|---|---|
| Geometric Transformation (0) | 2021.04.04 |
| Hough Transform (0) | 2021.04.01 |
| Image Resampling (Image pyramids) (0) | 2021.03.30 |
| SIFT (Scale invariant feature transform) (0) | 2021.03.26 |
