Hough Transform
1) 개요
- Generic framework for detecting a parametric model.
- Edges don't have to be connected.
- Lines can be occluded.
- Edges vote for the possible models.
- Robust to noise.
2) 원리

- Points(x, y) can be explained to parameter space m and b.
- Edges can be interpreted as many points in the image. If these points are quantized parameter space, there would be many points of intersection.
- A point of intersection means that a line passes through specific point on the image space(x,y).
- For example, if lines intersect at (m1, b1), y = m1*x + b line possibility of the existence would rise.
Algorithm
1. Quantize parameter space (m, c)
2. Create accumulator array A(m, c)
3. Set A(m, c) = 0 for all m, c
4. for each image edge (x_i, y_i), for each element in A(m, c)
if (m, c) lies on the line ( c= -x_i m + y_i), increment A(m, c) = A(m, c) + 1
5. Find local maxima in A(m, c)
3) Hough space

- the parameter space (m, c) can be infinite in contrast points. So, change it to finite space.
$$cos\theta x + sin\theta y = \rho,\;\; 0\leq \theta \leq 2\pi,\: 0\leq \rho \leq \rho_{max}$$
- a line becomes a point, a point becomes a wave in the hough space
4) Hough circles
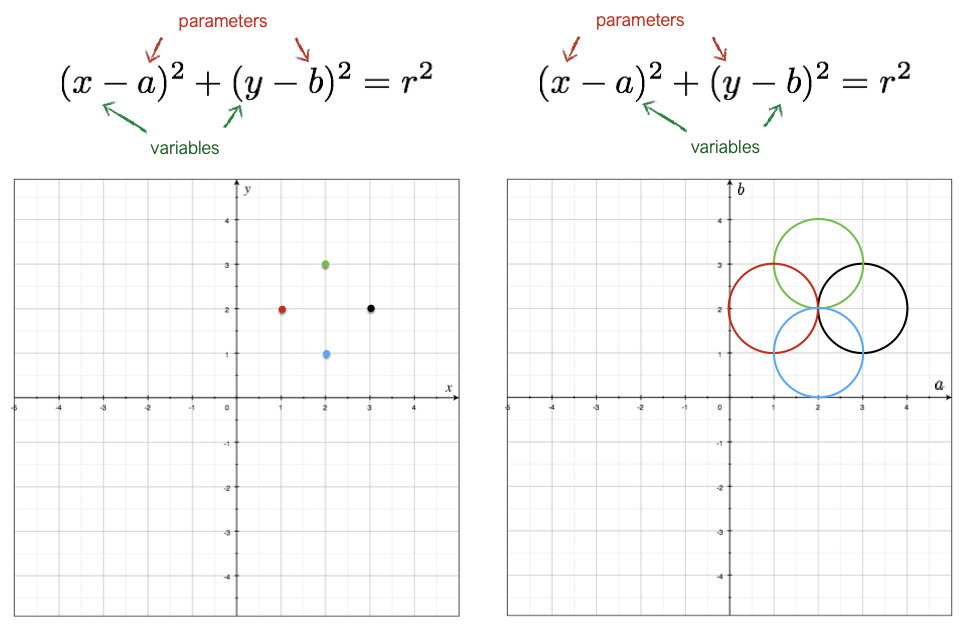
Code (Opencv)
1) HoughLines

img = cv2.imread('/users/sejongpyo/downloads/baduk.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edges = cv2.Canny(gray, 50, 150, apertureSize = 3)
lines = cv2.HoughLines(edges, 1, np.pi / 180, 200)
# (binary image, ρ accuracy, θ accuracy, threshold)
# threshold : minimum length of line that should be detected.
# returns (rho, theta)
for line in lines:
rho, theta = line[0]
a = np.cos(theta)
b = np.sin(theta)
x0 = a * rho
y0 = b * rho
x1 = int(x0 + 1000*(-b))
y1 = int(y0 + 1000*(a))
x2 = int(x0 - 1000*(-b))
y2 = int(y0 - 1000*(a))
cv2.line(img,(x1,y1),(x2,y2),(255,0,0),2)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
2) HoughLinesP
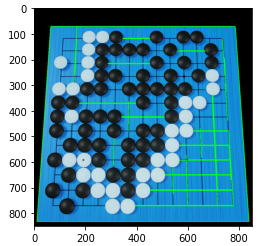
img = cv2.imread('/users/sejongpyo/downloads/baduk.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edges = cv2.Canny(gray, 50, 150, apertureSize = 3)
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(edges, 1, np.pi/180, 100, minLineLength=100, maxLineGap=10)
# minLineLength - Minimum length of line. Line segments shorter than this are rejected.
# maxLineGap - Maximum allowed gap between line segments to treat them as a single line.
for line in lines:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0]
cv2.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
3) HoughCircles
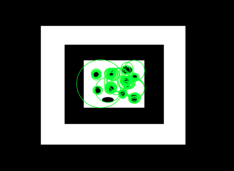
img = cv2.imread('/users/sejongpyo/downloads/con.jpg', 0)
img = cv2.medianBlur(img, 5)
cimg = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(img, cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 5, param1 = 50,
param2 = 30, minRadius = 0, maxRadius = 0)
# (네번째 : 검출한 원의 중심과의 최소거리값)
# (param1 : canny edge로부터 전달되는 parameter)
# (param2 : 작으면 오류가 높고 크면 검출률이 낮아짐)
# (minRadius, maxRadius : 0으로 지정지 사용 x)
circles = np.uint16(np.around(circles))
for i in circles[0, :]:
# outer
cv2.circle(cimg, (i[0], i[1]), i[2], (0, 255, 0), 5)
plt.imshow(cimg)
plt.show()ref.
'AI > Computer Vision' 카테고리의 다른 글
| RANSAC (0) | 2021.04.06 |
|---|---|
| Geometric Transformation (0) | 2021.04.04 |
| Image Resampling (Image pyramids) (0) | 2021.03.30 |
| SIFT (Scale invariant feature transform) (0) | 2021.03.26 |
| Harris Corner Detector (0) | 2021.03.24 |
