Image derivatives
1) 개요
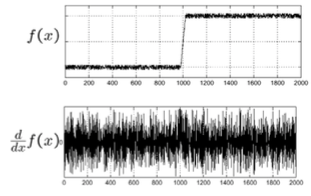
- Intuitively, the edges should have rapid change. By using Gaussian blurring, remove the noises first. The above image is the dreivative without applying Gaussian blurring.
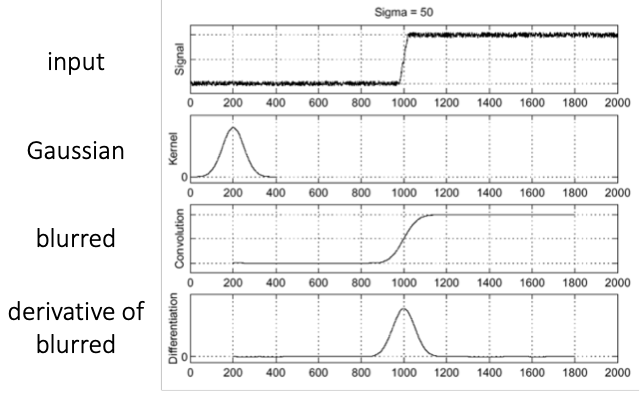
- Intensity changes over the image is important information.
- x and y derivatives of grayscale image can describe the intensity change.
- By gradient, get vector value from the image and can effectively use for edge detection.
2) Basic computation
- the image is in cumulative space. Its derivative is doing convolution using [-1, 1].
- After generate a matrix to compute the derivatives, do dot product with image matrix.
- Below tables are sample of computing the matrix.

- x derivatives compute by right side.
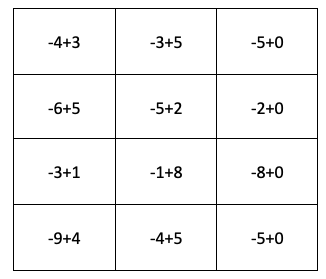
- y derivatives compute by down side.

3) Gradient magnitude and angle
- By using image gradient vector, we can get gradient magnitude and angle.
- gradient magnitude : describe how strong the image intensity change
$$\nabla I = \sqrt{I_{x}^{2} + I_{y}^{2}}$$
- angle (direction) : indicates direction of largest intensity change at each point (pixel)
$$\alpha (x, y) = arctan2(I_{y}, I_{x})$$
Gradient Filter
1) 개요
- There are various kinds of gradient filters. (High-pass filters; HPF)
- On behalf of a basic computation above, we can simply implement deriviates.
- It is critical to blur first.
2) Sobel

- Basic filter to extract edge from the images.
- Mostly, use with Gaussian smoothing.
- It relatively standardize projected pixel to extract brightness rate of change. So, strong to a noise.
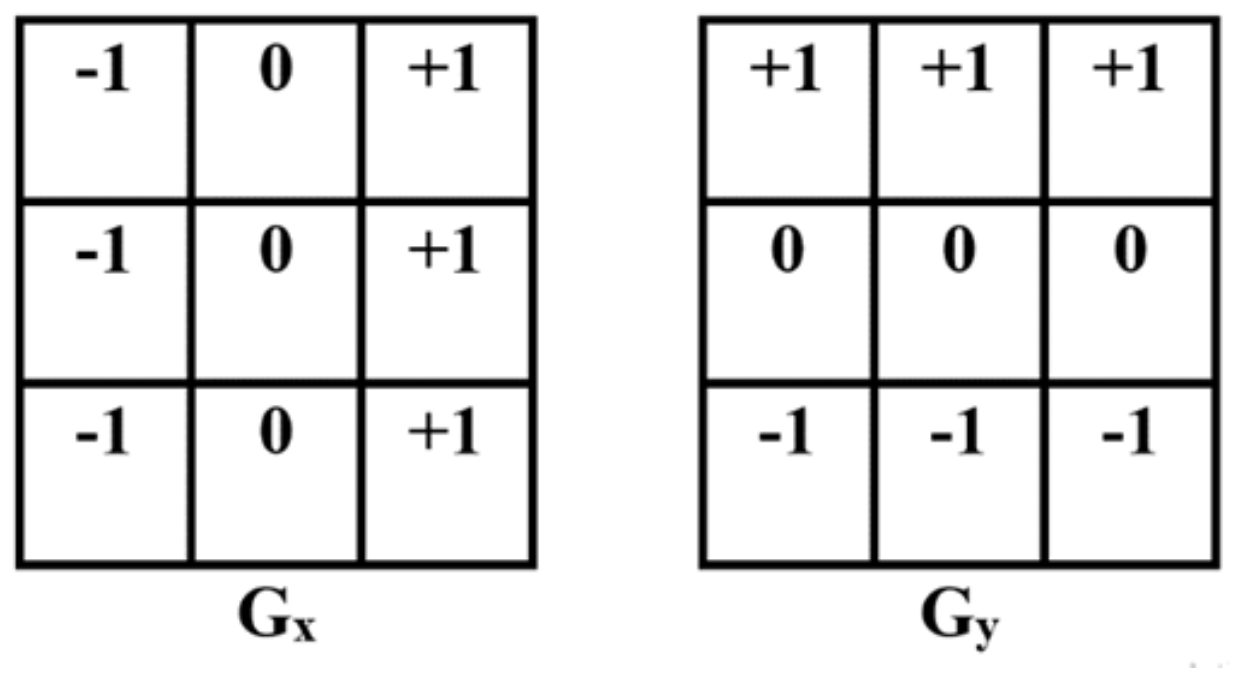
3) Prewitt
4) DoG filter (Derivative of Gaussian)
$$\frac{\partial}{\partial x} (h*f) = (\frac{\partial}{\partial x}h)*f$$

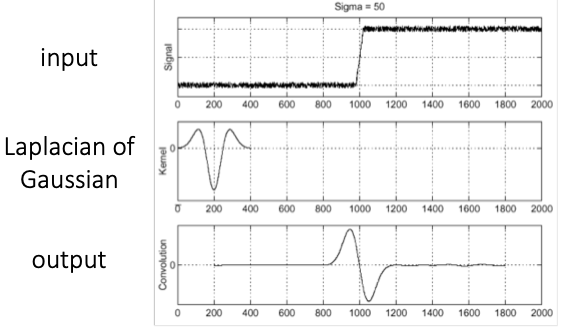
5) LoG filter (Laplacian of Gaussian)
$$f''(x) = \lim\frac{f(x+h)-2f(x)+f(x-h)}{h^{2}}$$
Example
1) Basic

# generate a matrix to compute the derivative in x-direction
Dx = -np.ones((n_col, n_col))
Dx = np.tril(Dx, 0)
Dx = np.triu(Dx, 0)
np.fill_diagonal(Dx[1:, :-1], 1)
# generate a matrix to compute the derivative in x-direction
Dy = -np.ones((n_row, n_row))
Dy = np.tril(Dy, 0)
Dy = np.triu(Dy, 0)
np.fill_diagonal(Dy[:-1, 1:], 1)
# compute the derivative of I with respect to x, y direction
Ix = I.dot(Dx)
Iy = Dy.dot(I)
# gradient magnitude
norm_gradient = np.square(Ix) + np.square(Iy)
2) SciPy (Sobel)
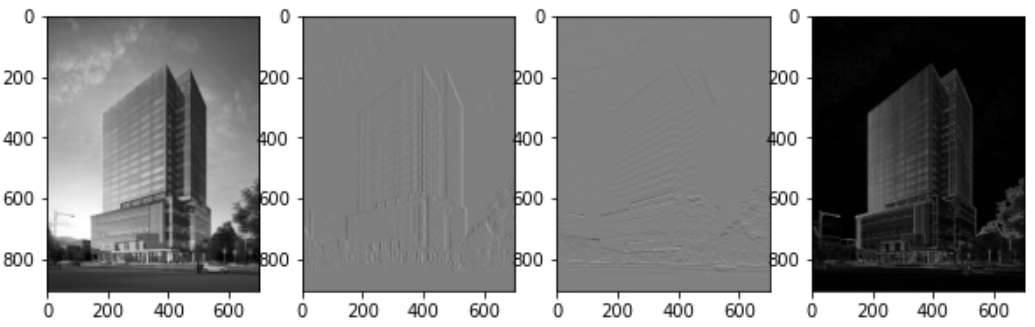
im = np.array(Image.open('/Users/sejongpyo/Downloads/building.jpg').convert('L'))
# Sobel derivative filters
imx = zeros(im.shape)
filters.sobel(im, 1, imx)
imy = zeros(im.shape)
filters.sobel(im, 0, imy)
magnitude = sqrt(imx**2 + imy**2)
f, ax = subplots(1, 4, figsize = (10, 7))
ax[0].imshow(im)
ax[1].imshow(imx)
ax[2].imshow(imy)
ax[3].imshow(magnitude)
plt.show()
3) OpenCV

img = cv2.imread('/Users/sejongpyo/downloads/baduk.png')
dst_x = cv2.Sobel(img, ddepth = -1, dx = 1, dy = 0, ksize = -1)
dst_y = cv2.Sobel(img, ddepth = -1, dx = 0, dy = 1, ksize = -1)참고
www.cs.cmu.edu/~16385/lectures/lecture2.pdf
opencv official document
'AI > Computer Vision' 카테고리의 다른 글
| SIFT (Scale invariant feature transform) (0) | 2021.03.26 |
|---|---|
| Harris Corner Detector (0) | 2021.03.24 |
| Morphology (0) | 2021.03.24 |
| Image filtering (Blurring images) (0) | 2021.03.23 |
| Histogram equalization (0) | 2021.03.23 |
