Model Ensemble
- 여러 모델들을 함께 사용하여 성능을 올린다.
- 앙상블 기법에는 voting, bagging, boosting, stacking 등이 있다.
Voting
1) 개요
- 다른 종류의 모델들의 예측값을 합쳐 최종 결과를 도출해내는 방법이다.
- continuous outputs : combine it by averaging
- class label outputs : combine it by voting
- Voting 종류는 크게 hard, soft, weighted로 나뉜다.
2) Hard voting
- Unanimous voting : 만장일치일 때만 선택한다.
- Majority voting : 제일 많이 나온 것을 선택한다.
$$Ensemble(\hat{y})=argmax(\sum_{j=1}^{n}I(\hat{y}_{j} = i),\: i \in (0, 1))$$
3) Soft voting
- 각 class별로 모델들이 예측한 확률의 평균 값을 계산하여 가장 높은 class 선택
$$Ensemble(\hat{y})=argmax(\frac{1}{n}\sum_{j=1}^{n}P(y=i)),\: i \in (0, 1))$$
4) Weighted voting
- 각각의 모델별로 class에 대한 가중치를 준다.
-아래 식은 training accuracy를 사용하여 가중평균을 계산한 방법이다.
$$Ensemble(\hat{y})=argmax(\frac{\sum_{j=1}^{n}(TrainAcc_{j})\cdot I(\hat{y}_{j} = i)}{\sum_{j=1}^{n}(TrainAcc_{j})}),\: i \in (0, 1))$$
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
import numpy as np
clf1 = LogisticRegression(solver = 'liblinear', penalty = 'l2', C = 0.001, random_state = 1)
clf2 = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth = 1, criterion = 'entropy', random_state = 0)
clf3 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 1, p = 2, metric = 'minkowski')
pipe1 = Pipeline([['sc', StandardScaler()], ['clf', clf1]])
pipe3 = Pipeline([['sc', StandardScaler()], ['clf', clf3]])
# Votingclassifier / votingregressor
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier
models = [pipe1, clf2, pipe3]
hard_vote = VotingClassifier(models, voting='hard')
asdf = cross_val_score(estimator = hard_vote, X = X_train, y= y_train,
cv = 10, scoring = 'roc_auc')
hard_vote.fit(X_train, y_train)Bagging (Bootstrap Aggregating)
1) 개요
- 각각의 bootstrap sample로 부터 생성된 모델을 합침
- voting은 모델의 종류가 다양하지만 bagging은 동일 알고리즘을 여러 개 사용한다.
- 대표적으로 Randomforest가 있다. (sjpyo.tistory.com/41?category=956366)
Random Forest
Random Forest (결정트리) 1) 개요 - decision tree의 ensemble로 decision tree들의 예측을 종합한다. - decision tree의 low computational complexity (모델 구축 속도), nonparametric 특성으로 base 모델로..
sjpyo.tistory.com
2) Bootstrap
- sampling 방법으로 각 모델은 다른 훈련 데이터셋을 이용
- 복원추출(같은 샘플이 여러 개 있을 수 있다)을 통해 원래 데이터의 수와 동일한 크기를 sampling
- 이론적으로 1 개의 샘플이 한번도 sampling 되지 않을 확률
$$p = (1-\frac{1}{N})^{N} \rightarrow \lim_{N\rightarrow \infty}(1-\frac{1}{N})^{N} = e^{-1} = 0.368$$
3) Aggregating
- 위의 voting 방식을 사용해 합산한다.
Random subspace
1) 원래 변수들 중에서 모델 구축에 사용할 입력 변수를 무작위 선택 (모든 변수보다 적은 변수 선택)
2) 선택된 입력 변수 중 분할될 변수 선택
3) full-grown tree가 될 때까지 반복
ex) 변수 1, 2, 3, 4, 5번이 있을 때, (1)에 의해 2, 3, 5번이 무작위로 선택됐다. 이때 선택된 3가지 중 impurity index가 가장 이상적
인 변수를 선택하고 이를 반복한다.
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'entropy', random_state = 1, max_depth = None)
bag = BaggingClassifier(base_estimator = tree, n_estimators = 500, max_samples = 1.0,
max_features = 1.0, bootstrap = True,
bootstrap_features = False, n_jobs = -1, random_state = 1)Boosting
1) 개요
- weak learner (약한 학습기) 라는 매우 간단한 분류기이다.
- 순차학습을 통해 잘못 분류된 샘플에 가중치를 부여해 오차를 줄여나간다.
- 순차적으로 모델을 구축하기 때문에 순서가 매우 중요하다.
- 대표적으로 AdaBoost 알고리즘이 있으며, 이후 Xgboost, LightGBM, Catboost 등이 등장했다.
2) Adaboost (Adaptive Boosting)
- training error 크면 가중치를 높이고, 작으면 가중치를 낮춰 오분류한 관측치에 무게를 둔다.
- 이를 기반으로 다음 단계에서 사용할 dataset을 구성하고 이를 반복하여 최종 결과를 예측한다.
- AdaBoost algorithm
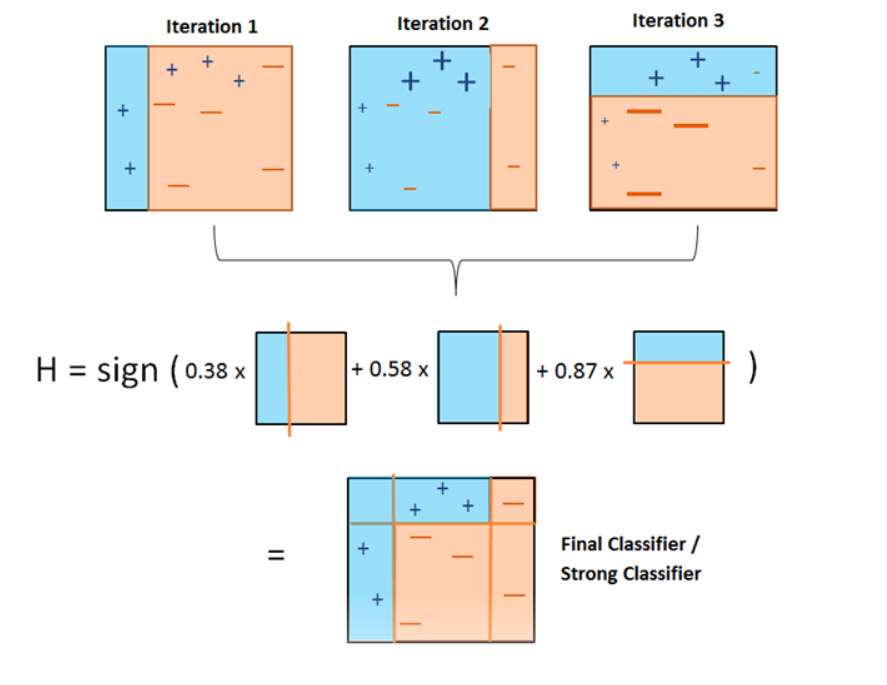
(1) impose equal weight initially
$$W_{i} = \frac{1}{n}, \: i=1,2,...,n$$
(2) find h(x) that minimizes L (weighted loss function); 아래의 예는 3개 오분류한 경우
$$L_{j} = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n}W_{i}I(y_{i}\neq h_{j}(x))}{\sum_{i=1}^{n}W_{i}}=\frac{0.1 \times 3}{0.1 \times 10}=0.3$$
(3) calculate each classes' weights
$$a_{1} = log(\frac{1-L_{j}}{L_{j}}) = log(\frac{1 - 0.3}{0.3})=\approx 0.37$$
(4) update samples weights
$$W_{c} = W_{i}e^{a_{j}I(y_{i} \neq h_{1}(x))} = 0.1e^{0.37 \times 0}=0.1$$
$$W_{nc} = 0.1e^{0.37\times 1} = 0.14$$
(5) step 2로 돌아가서 다시 수행한다.
(6) Final step
$$h(x) = sign[\sum_{i=1}^{m}a_{j}h_{j}(x)]$$
Indicator function : if x true -> 1, if x false -> 0
$$I(y_{i} \neq h_{i}(x))$$
- 코드 예시
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'entropy',
random_state =1, max_depth = 1)
ada = AdaBoostClassifier(base_estimator = tree, n_estimators = 500,
learning_rate = 0.1, random_state = 1)
ada = ada.fit(X_train, y_train)
3) GBM (Gradient Boosting Machines)
- base 모델로 decision tree 사용
- 순차적으로 residual (y - 예측y)값을 다시 fitting해가며 줄여가는 방식이다.
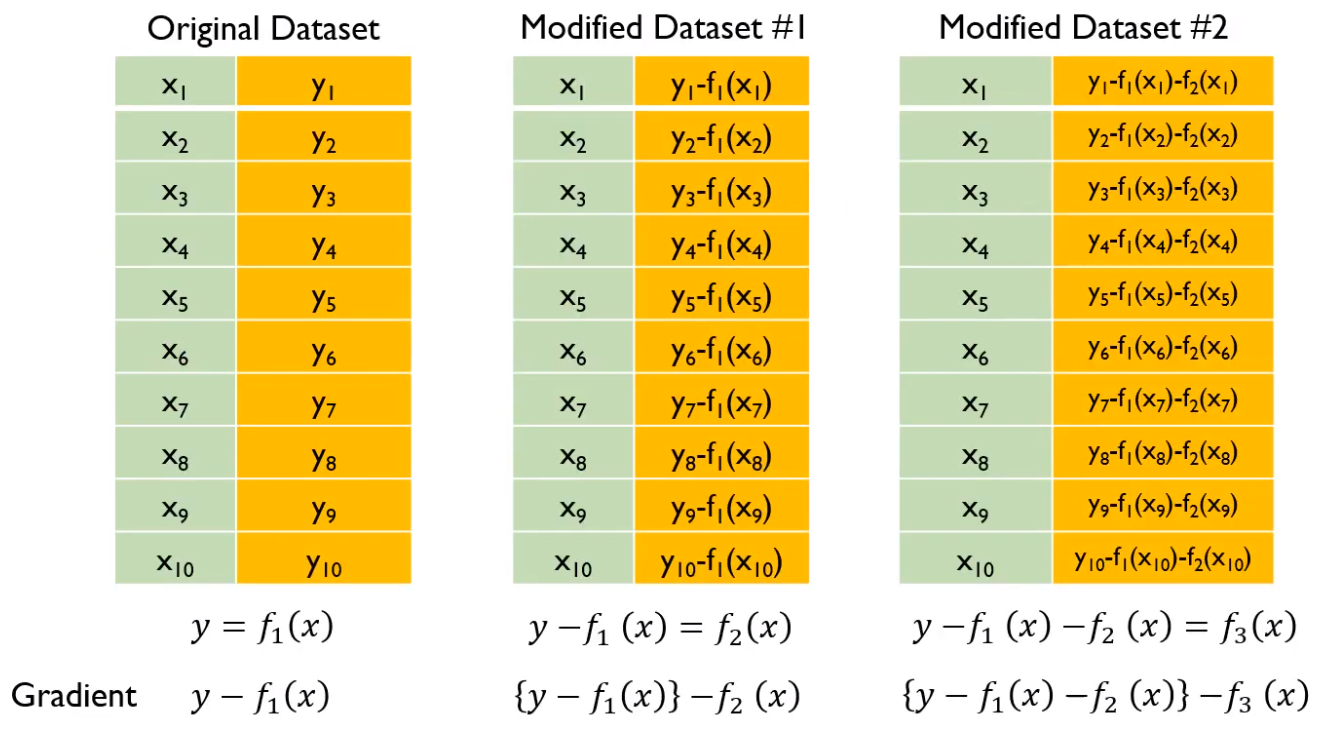
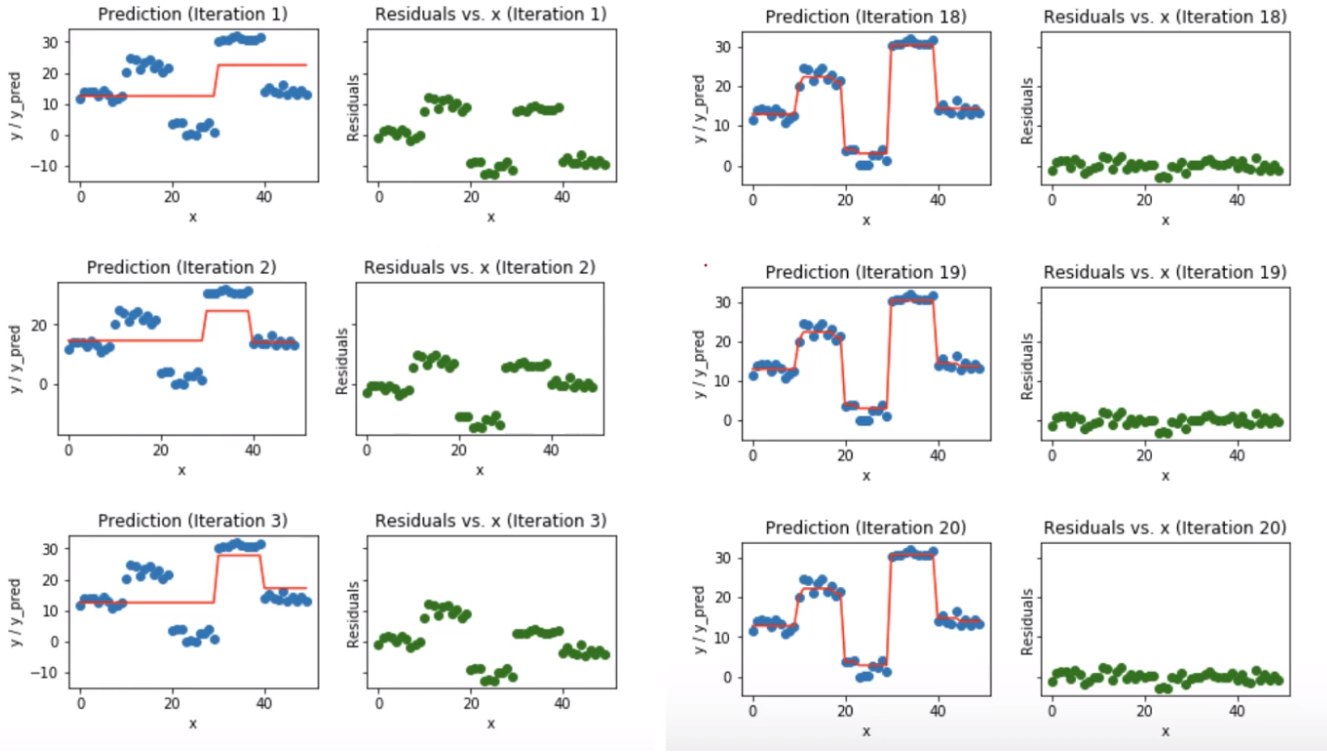
- residual & gradient
$$L=\frac{1}{2}\sum_{i=1}^{n}(y_{i}-f(x_{i}))^{2}$$
$$Gradient \Rightarrow \frac{\partial L}{\partial f(x_{i})}=-(y_{i}-f(x_{i})) = residual$$
- 코드 예시
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
gbrt = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators = 20, random_state = 42)
gbrt.fit(X_train, y_train)
gbrt_train_score = gbrt.score(X_train, y_train)
gbrt_test_score = gbrt.score(X_test, y_test)참고
머신러닝 교과서 (길벗)
machinelearningmastery.com/voting-ensembles-with-python/
고려대 김성범 교수님 유튜브 www.youtube.com/channel/UCueLU1pCvFlM8Y8sth7a6RQ
medium.com/mlreview/gradient-boosting-from-scratch-1e317ae4587d
'AI > Machine Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Clustering Analysis (0) | 2021.02.28 |
|---|---|
| Linear regression (0) | 2021.02.26 |
| Model evaluation metrics (0) | 2021.02.23 |
| Validation (Cross-val, learning-curve, GridSearch) (0) | 2021.02.23 |
| Model pipeline (0) | 2021.02.22 |
